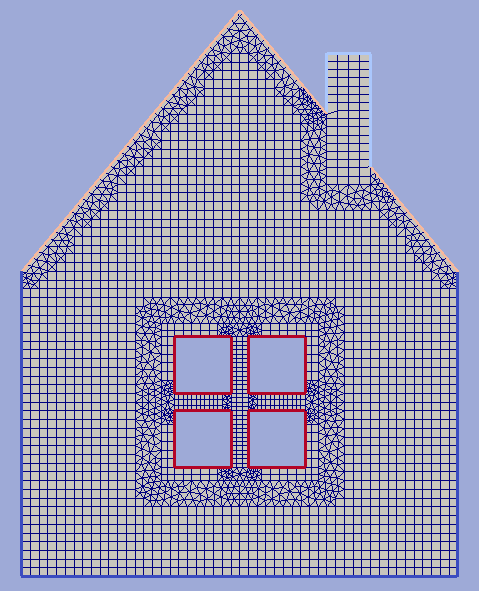
Example 2¶
Here we mesh a house-like domain keeping separate boundary features for edges which lie on the roof, window spans and the tube.
from hybmeshpack import hmscript as hm
# This script was created for hybmesh 0.2.1.
# If running version of hybmesh is not compatible with this version
# an exception will be raised at this line.
hm.check_compatibility("0.2.1", 2)
# Register separate boundary types for edges on tube, roof and window.
# All other boundary edges will get default 0 boundary type
btube = hm.add_boundary_type(1, "Tube")
broof = hm.add_boundary_type(2, "Roof")
bwindow = hm.add_boundary_type(3, "Window")
# First we create a house silhouette and assign boundary types for it.
# They will be carried to all grids derived from this contour
house_cont = hm.create_contour([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 0.7], [0.5, 1.3],
[0, 0.7], [0, 0]], [0, 0, broof, broof, 0])
# Build a background rectangular mesh and cut a house silhouette from it.
# Now 'house' grid bears boundary features of 'house_cont'
back_grid = hm.add_unf_rect_grid([0, 0], [1, 2], 50, 100)
house = hm.exclude_contours(back_grid, house_cont, "outer")
# A set of ugly cells near the roof appeared as a result of previous operation.
# To get rid of 'em we build a short single layered boundary grid near the
# roof section and make a union. 'roof' grid inherits its boundary types
# from 'house_cont' which is its source and delivers 'em to 'house_wroof' object.
oproof = hm.BoundaryGridOptions(
house_cont,
start_point=[1, 0.7], end_point=[0, 0.7],
partition=[0, 0.01], bnd_step=0.02)
roof = hm.build_boundary_grid([oproof])
house_wroof = hm.unite_grids(house, [(roof, 0.03)])
# Build a tube rectangle and set all boundary edges to 'Roof' type
gtube = hm.add_unf_rect_grid([0, 0], [0.1, 0.3], 4, 16)
hm.set_boundary_type(gtube, btube)
hm.move_geom(gtube, 0.7, 0.9)
# after combining of 'house_wroof' and 'gtube' the resulting grid
# boundary edges will get their features from both parent grids
house_wtube = hm.unite_grids(house_wroof, [(gtube, 0.05)])
# first we create an outer window frame by building an external
# boundary grid around square contour
win_cont = hm.add_rect_contour([-0.15, -0.15], [0.15, 0.15])
op1 = hm.BoundaryGridOptions(win_cont, bnd_step=0.02, direction='right')
op1.uniform_partition(0.03, 2)
win_frame1 = hm.build_boundary_grid([op1])
# now we create a internal window frames
win_frame2 = hm.add_unf_rect_grid([-0.02, -0.15], [0.02, 0.15], 3, 30)
[win_frame3] = hm.copy_geom([win_frame2])
hm.rotate_geom(win_frame2, 90)
# to assemble a window we make an superposition of internal frames to outer one
# and assigns 'Window' boundary type to the whole resulting grid.
window = hm.unite_grids(win_frame1, [(win_frame2, 0.02), (win_frame3, 0.02)])
hm.set_boundary_type(window, bwindow)
# finally we move window to its position according to house and
# impose it to it. Note that in order to purge area within window spans
# option 'empty_holes=True' is used.
hm.move_geom(window, 0.5, 0.4)
house_final = hm.unite_grids(house_wtube, [(window, 0.05)], empty_holes=True)
# now we can check quality of resulting grid by calculating its skewness
skew = hm.skewness(house_final)
print 'maximum skew value is %f' % skew['max_skew']
if (skew['ok']):
print 'resulting grid has no bad cells'
else:
print '%i cells have large skew coefficient' % len(skew['bad_cells'])
# save grid and contour with boundary features to vtk
hm.export_grid_vtk(house_final, "house_grid.vtk")
hm.export_contour_vtk(house_final, "house_contour.vtk")